가장 가까운 기-종점 매트릭스 위치 (QGIS3)¶
In the previous tutorial, Basic Network Visualization and Routing (QGIS3), we learned how to build a network and calculate the shortest path between 2 points. We can apply that technique to many different types of network-based analysis. One such application is to compute Origin-Destination Matrix or OD Matrix. Given a set of origin points and another set of destination points, we can calculate the shortest path between each origin-destination pairs and find out the travel distance/time between them. Such analysis is useful to locate the closest facility to any given point. For example, a logistics company may use this analysis to find the closest warehouse to their customers to optimize delivery routes. Here we use the Distance Matrix algorithm from QGIS Network Analysis Toolbox (QNEAT3) plugin to find the nearest health facility to each address in the city.
참고
This tutorial shows how to use your own network data to compute an origin-destination matrix. If you do not have your own network data, you can use ORS Tools Plugin and algorithm to do a similar analysis using OpenStreetMap data. See Openrouteservice를 이용한 서비스 영역 분석(QGIS3) to learn how to use ORS Tools plugin.
개요¶
워싱턴 DC의 레이어 2개를 사용합니다 - 점 데이터는 주소 정보이고 다른 점 데이터는 정신의료시설을 표시하는 정보입니다 - 각 지점에서 가장 짧은 노선으로 갈 수 있는 최적 경로를 찾아봅시다.
이 예제에서 필요한 다른 기술¶
Extract a random sample from a point layer.
QGIS 레이어에서 SQL 쿼리를 이용하여 가상레이어 사용하기
데이터 획득¶
Open Data Catalog. 이곳에서 콜롬비아 정부가 무료로 제공하는 다양한 데이터를 만나보실 수 있습니다.
다음의 쉐이프파일을 내려받기해주세요.
아래 링크에서 이번예제에 사용되는 샘플파일을 쉽게 내려받을 수 있습니다:
Community Based Service Provider.zip
데이터 출처: [DCOPENDATA]
설정¶
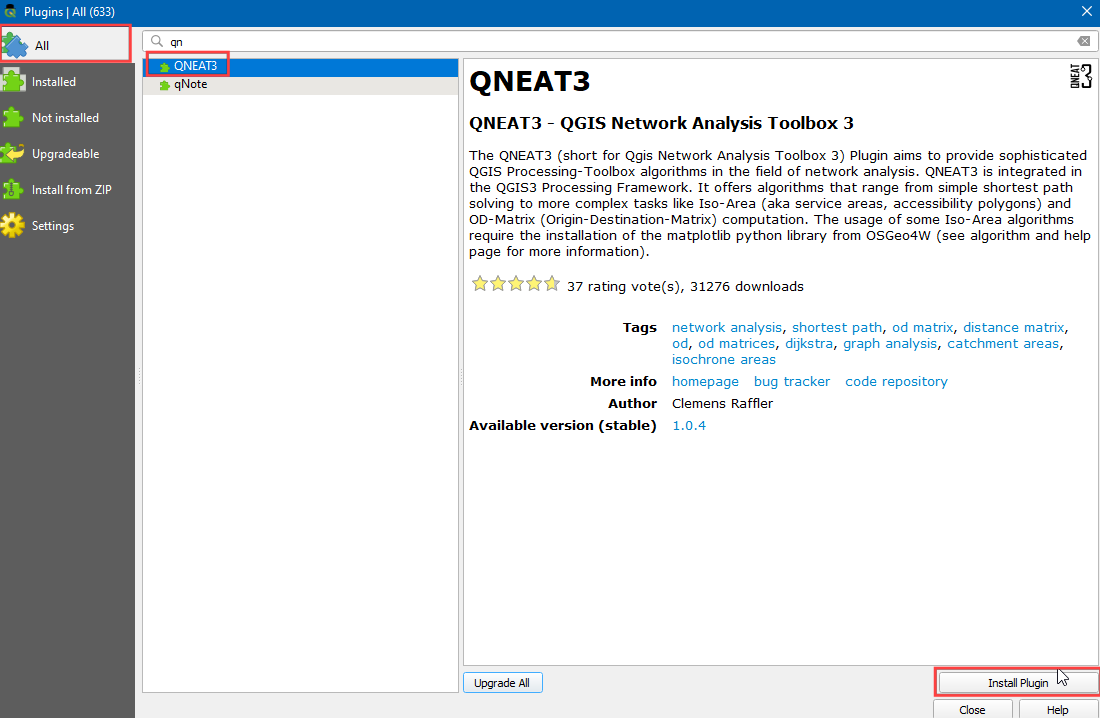
Visit . Select :guilabel:` All` Search for QNEAT3 plugin and install it. Click Close.
과정¶
Locate the
Community_Based_Service_Providers.zipfile, expand it and addCommunity_Based_Service_Providers.shpto the canvas. We will select only those centres providing facilities to adults. Right-click on theCommunity_Based_Service_Providers.shplayer and select Filter.
It will open a Query Builder dialog box. Enter the following query in the :guilabel:` Filter Expression` Click Run.
"PROVIDER_T" IN ('Adult','Adult & Child')
Next, locate the
Roadway_Block.zipfile, expand it and add theRoadway_Block.shp. Similarly, locate theAddress_Points.zipfile, expand it and add theAddress_Points.shp. You will see a lot of points around the city. Each point represents a valid address. We will select 1000 points randomly. This technique is called random sampling. Go to .
Search for and locate the algorithm.
Select
Address_Pointsas the Input layer,Number of featureas the Method and, enter1000in the Number/percentage of features. In the Extracted (random) choose the...and click Save to a file. Now choose the directory and enter the name asaddress_point_subset.shpand click Run.
참고
As the algorithm will extract 1000 random points from the given data set, to replicate the exact points used in this exercise you can download the subset file which we got during the execution of the algorithm here address_point_subset.zip . After downloading load address_point_subset.shp layer into QGIS.
A new layer
address_point_subsetwill be added to the Layers panel, you can turn off the visibility ofAddress_Pointsaddress points layer. Let’s rename this layer asorigin_points. Right-click on theaddress_point_subsetlayer and select Rename layer.
Similarly, rename the
Community_Based_Service_Providerlayers representing the health facilities asdestination_points. Naming the layers this way makes it easy to identify them in subsequent processing. Further we will open processing toolbox to create the distance matrix using origin and destination layers.
Locate the algorithm. If you do not see this algorithm in the toolbox, make sure you have installed the QNEAT3 plugin.
This algorithm helps find the distances along with the network between selected origin and destination layers. Select
Roadway_Blockas the Network layer. Selectorigin_pointsas the From-Points layer andOBJECTIDas the Unique Point ID field. Similarly, setdestination_pointsas the To-Points Layer andOBJECTIDas the Unique Point ID field. Set the Optimization Criterion asShortest Path (distance optimization).
As many streets in the network are one-way, we need to set the Advanced parameters to specify the direction. See Basic Network Visualization and Routing (QGIS3) for more details on how these attributes are structured. We also have an option to select geometry style of the generated matrix. We are having a road network with direction information so we can generate matrix by folling the route. Choose
Matrix geometry follows routes. ChooseSUMMARYDIRas the Direction field. EnterOBas the Value for the forward direction,IBas the Value for backward direction, andBDas the Value for the both direction. Set the Topology tolerance as0.000150. Keep other options to their default values and click Run.
A new table layer called
Output OD Matrixwill be added to the Layers panel. Right-click and select Open Attributes Table. You will see that the table contains 67000 rows. We had 67 origin points and 1000 destination points - so the output contains 67x1000 = 67000 pairs of origins and destination. Thetotal_costcolumn contains distance in meters between each origin point to every destination point.
For this tutorial, we are interested in only the destination point with the shortest distance. We can create a SQL query to pick the destination with the least
total_costamong all destinations. Go to .Search for and locate the .
In Additional input data sources select
...and check the Output OD Matrix and, click OK. Now click the Summation under SQL query. Enter the following query in SQL query dialog box. Entergeometryas the Geometry field and, selectLineStringas the Geometry type. Click Run.
select origin_id, destination_id, min(total_cost) as shortest_distance, geometry from input1 group by origin_id
A new virtual layer
SQL Outputwill be added to the Layers panel. This Layer has the result of our analysis. Nearest service provider for each of the 1000 origin points.
 Ujaval Gandhi
Ujaval Gandhi
If you want to give feedback or share your experience with this tutorial, please comment below. (requires GitHub account)