Scriptare în Python pentru Cadrul de Procesare (QGIS3)¶
Se pot crea script-uri pyqgis independente, care pot fi executate prin intermediul Consolei Python din QGIS. Cu puține modificări, puteți rula script-urile prin intermediul Cadrului de Procesare. Acest lucru are mai multe avantaje. În primul rând, preluarea datelor de la utilizator și scrierea fișierelor de ieșire este mult mai ușoară, deoarece Cadrul de Procesare oferă o interfață de utilizator standardizată pentru acestea. În al doilea rând, având script-ul în Bara de Instrumente de Procesare, este posibil ca acesta să facă parte din orice Model de Procesare sau să ruleze în serie, pentru mai multe intrări. Acest tutorial vă arată cum să scrieți un script Python personalizat, care să facă parte din Cadrul de Procesare din QGIS.
Notă
The Processing API was completely overhauled in QGIS3. Please refer to this guide for best practices and tips.
Privire de ansamblu asupra activității¶
Our script will perform a dissolve operation based on a field chosen by the user. It will also sum up values of another field for the dissolved features. In the example, we will dissolve a world shapefile based on a CONTINENT attribute and sum up POP_EST field to calculate total population in the dissolved region.
Obținerea datelor¶
We will use the Admin 0 - Countries dataset from Natural Earth.
Download the Admin 0 - countries shapefile..
Sursa de Date [NATURALEARTH]
Pentru comoditate, puteți descărca de mai jos un fișier geopackage care conține straturile în cauză:
Procedura¶
In the QGIS Browser Panel, locate the directory where you saved your downloaded data. Expand the
zipor thegpkgentry and select thene_10m_admin_0_countrieslayer. Drag the layer to the canvas.
Go to . Click the Scripts button in the toolbar and select Create New Script from Template.
The template contains all the boilerplate code that is required for the Processing Framework to recognize it as a Processing script, and manage inputs/outputs. Let’s start customizing the example template to our needs. First change the class name from
ExampleProcessingAlgorithmtoDissolveProcessingAlgorithm. This name also needs to be updated in thecreateInstancemethod. Add a docstring to the class that explains what the algorithm does.
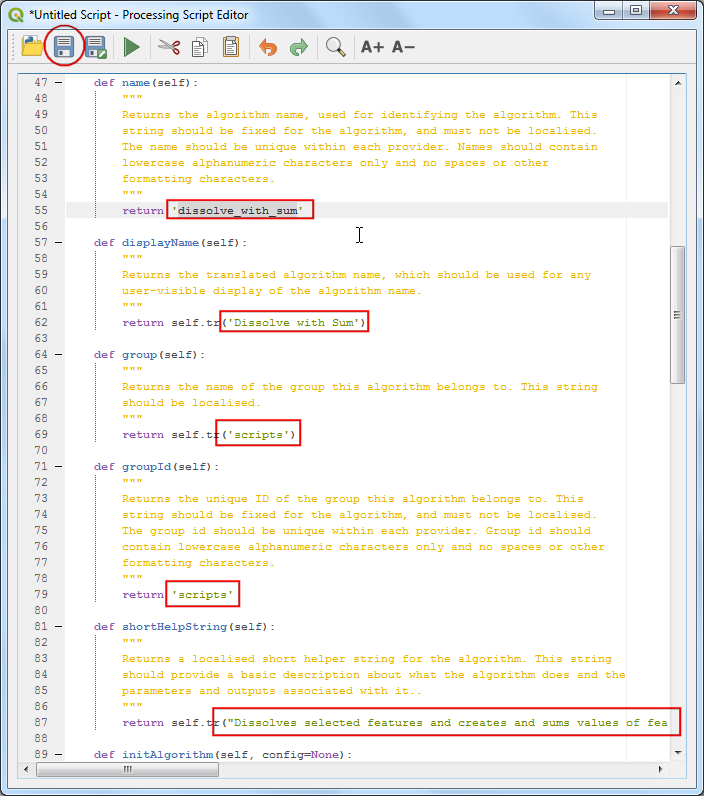
As you scroll down, you will see methods that assign name, group, description etc. to the script. Change the return values for name method to be
dissolve_with_sum, displayName method toDissolve with Sum, group method and groupId method toscripts. Change the return value of shortHelpString method to a description that will appear to the user. Click the Save button.
Name the script
dissolve_with_sumand save it at the default location under folder.
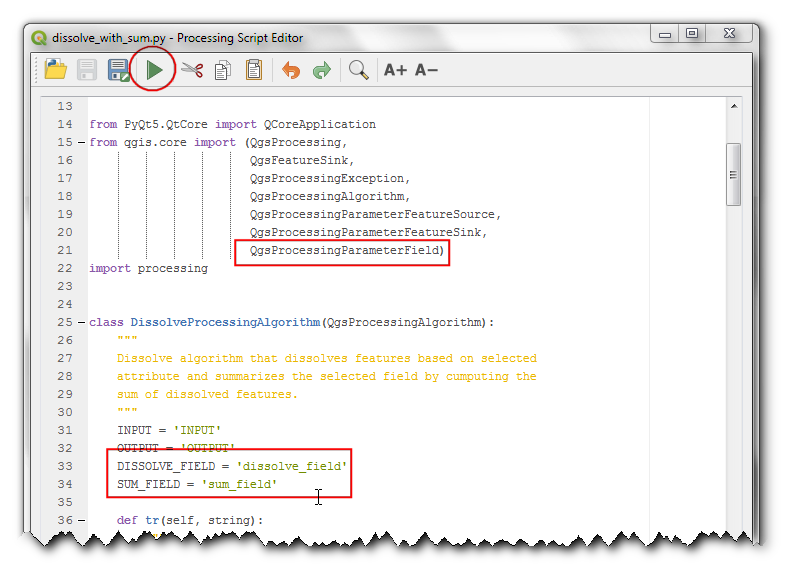
Now we will define the inputs for the script. The template already contains a definition of an
INPUTVector Layer and aOUTPUTlayer. We will add 2 new inputs which allows the user to select aDISSOLVE_FIELDand aSUM_FIELD. Add a new import at the top and the following code in theinitAlgorithmmethod. Click the Run button to preview the changes.
from qgis.core import QgsProcessingParameterField
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterField(
self.DISSOLVE_FIELD,
'Choose Dissolve Field',
'',
self.INPUT))
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterField(
self.SUM_FIELD,
'Choose Sum Field',
'',
self.INPUT))
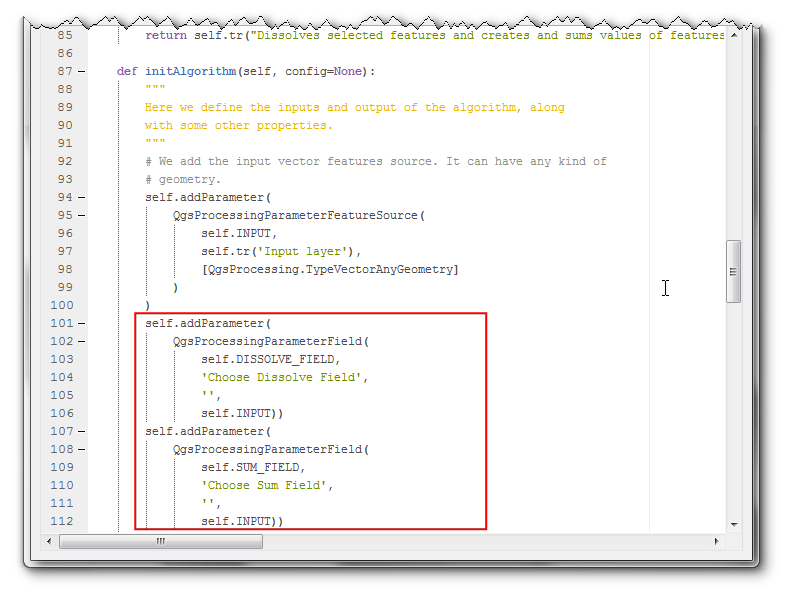
You will see a Dissolve with Sum dialog with our newly defined inputs. Select the
ne_10m_admin_0_countrieslayer as Input layer`. As both Dissolve Field and Sum Fields are filtered based on the input layer, they will be pre-populated with existing fields from the input layer. Click the Close button.
Now we define our custom logic for processing data in the
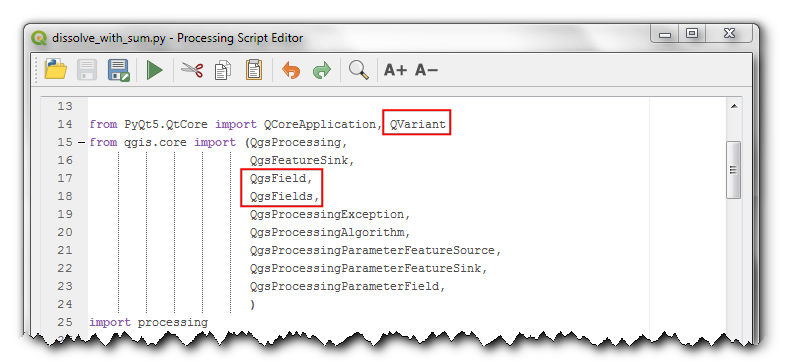
processAlgorithmmethod. This method gets passed a dictionary calledparameters. It contains the inputs that the user has selected. There are helper methods that allow you to take these inputs and create appropriate objects. We first get our inputs usingparameterAsSourceandparameterAsStringmethods. Next we want to create a feature sink where we will write the output. QGIS3 has a new class calledQgsFeatureSinkwhich is the preferred way to create objects that can accept new features. The output needs only 2 fields - one for the value of dissolved field and another for the sum of the selected field.
from PyQt5.QtCore import QVariant
from qgis.core import QgsField, QgsFields
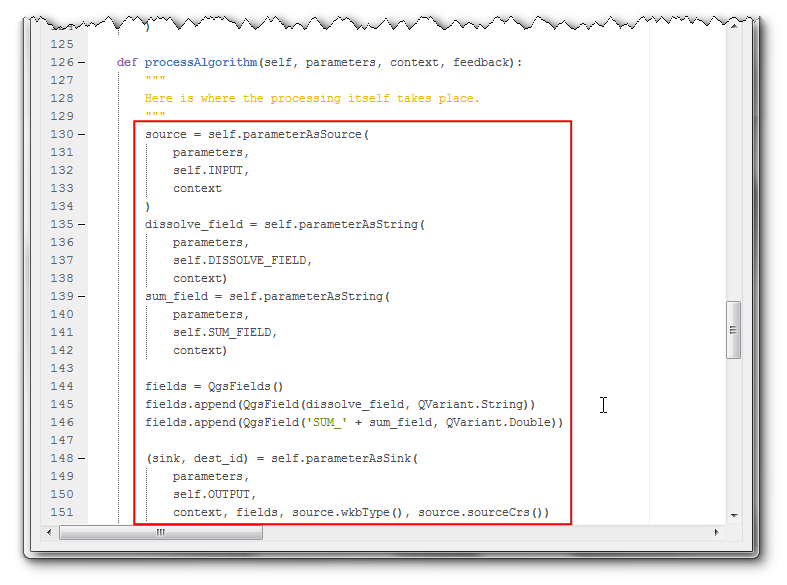
source = self.parameterAsSource(
parameters,
self.INPUT,
context)
dissolve_field = self.parameterAsString(
parameters,
self.DISSOLVE_FIELD,
context)
sum_field = self.parameterAsString(
parameters,
self.SUM_FIELD,
context)
fields = QgsFields()
fields.append(QgsField(dissolve_field, QVariant.String))
fields.append(QgsField('SUM_' + sum_field, QVariant.Double))
(sink, dest_id) = self.parameterAsSink(
parameters,
self.OUTPUT,
context, fields, source.wkbType(), source.sourceCrs())
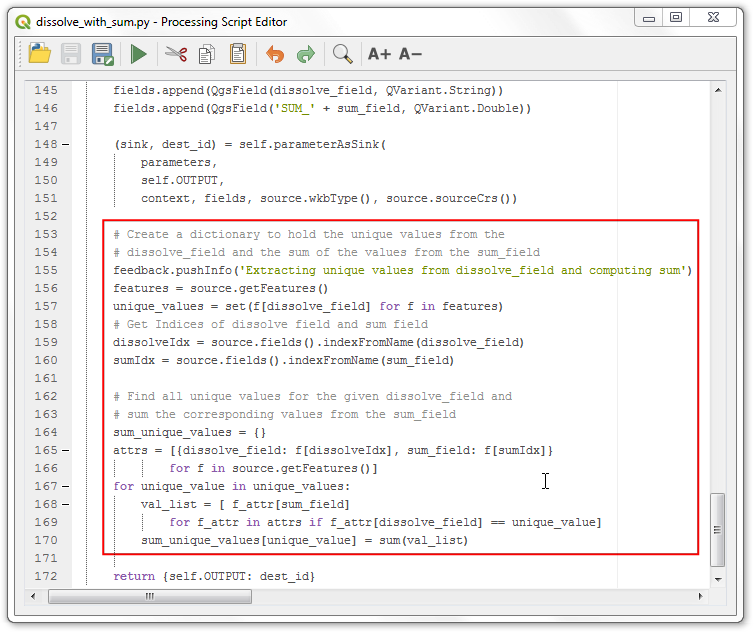
Now we will ready the input features and create a dictionary to hold the unique values from the dissolve_field and the sum of the values from the sum_field. Note the use of
feedback.pushInfo()method to communicate the status with the user.
feedback.pushInfo('Extracting unique values from dissolve_field and computing sum')
features = source.getFeatures()
unique_values = set(f[dissolve_field] for f in features)
# Get Indices of dissolve field and sum field
dissolveIdx = source.fields().indexFromName(dissolve_field)
sumIdx = source.fields().indexFromName(sum_field)
# Find all unique values for the given dissolve_field and
# sum the corresponding values from the sum_field
sum_unique_values = {}
attrs = [{dissolve_field: f[dissolveIdx], sum_field: f[sumIdx]} for f in source.getFeatures()]
for unique_value in unique_values:
val_list = [ f_attr[sum_field] for f_attr in attrs if f_attr[dissolve_field] == unique_value]
sum_unique_values[unique_value] = sum(val_list)
Next, we will call the built-in processing algorithm
native:dissolveon the input layer to generate the dissolved geometries. Once we have the dissolved geometries, we iterate through the output of the dissolve algorithm and create new features to be added to the output. At the end we return thedest_idFeatureSink as the output. Now the script is ready. Click the Run button.
Notă
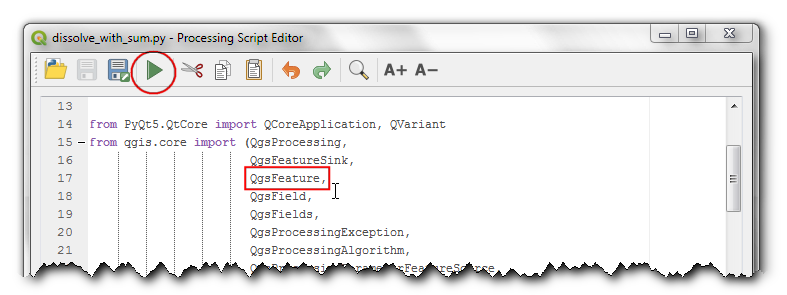
Notice the use of parameters[self.INPUT] to fetch the input layer from the parameters dictionary directly without defining it as a source. As we are passing the input object to the algorithm without doing anything with it, it’s not necessary to define it as a source.
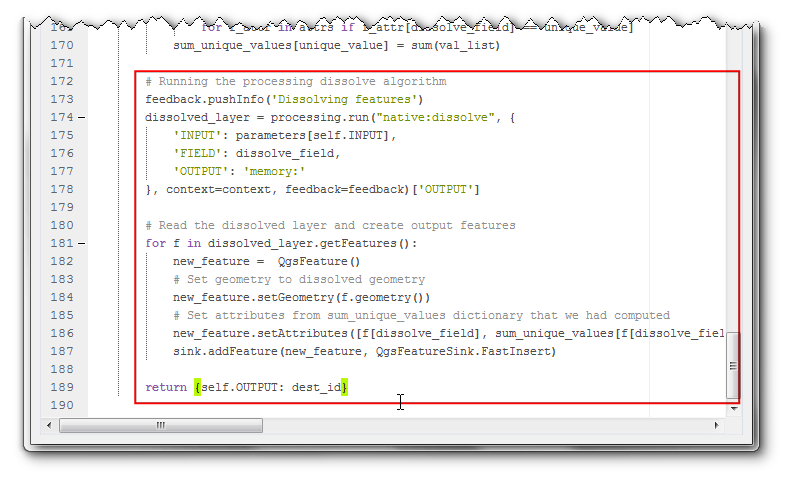
from qgis.core import QgsFeature
# Running the processing dissolve algorithm
feedback.pushInfo('Dissolving features')
dissolved_layer = processing.run("native:dissolve", {
'INPUT': parameters[self.INPUT],
'FIELD': dissolve_field,
'OUTPUT': 'memory:'
}, context=context, feedback=feedback)['OUTPUT']
# Read the dissolved layer and create output features
for f in dissolved_layer.getFeatures():
new_feature = QgsFeature()
# Set geometry to dissolved geometry
new_feature.setGeometry(f.geometry())
# Set attributes from sum_unique_values dictionary that we had computed
new_feature.setAttributes([f[dissolve_field], sum_unique_values[f[dissolve_field]]])
sink.addFeature(new_feature, QgsFeatureSink.FastInsert)
return {self.OUTPUT: dest_id}
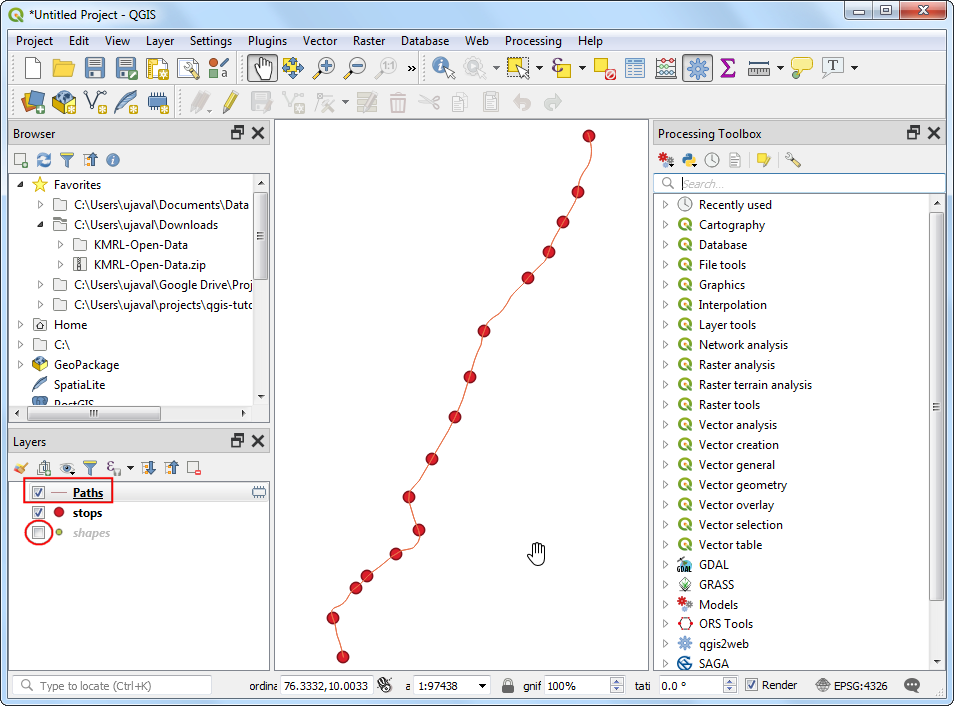
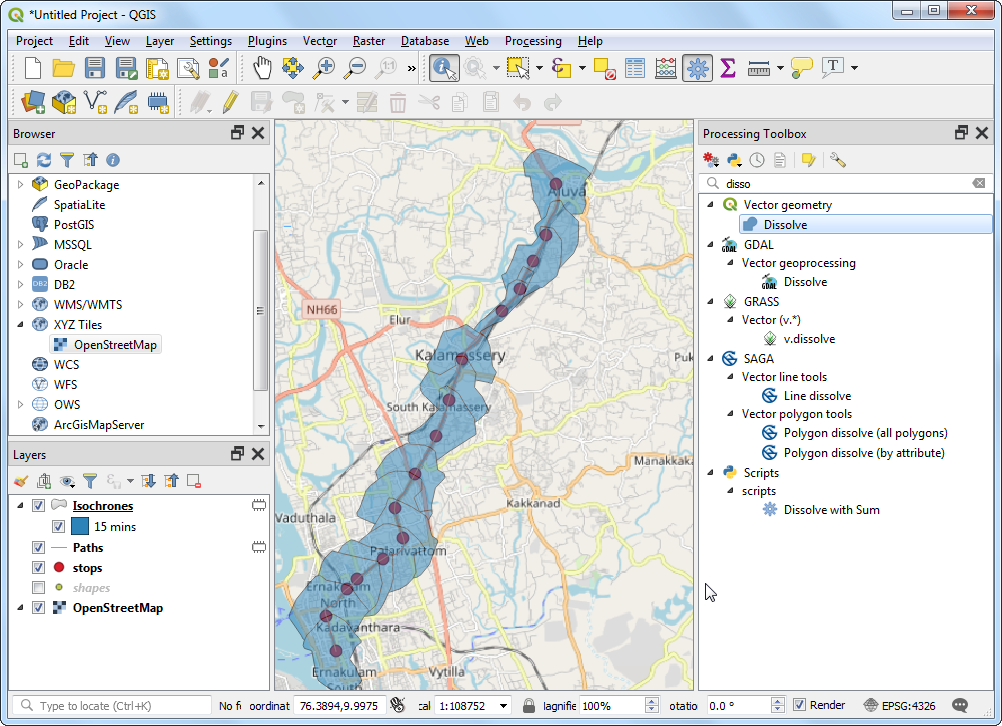
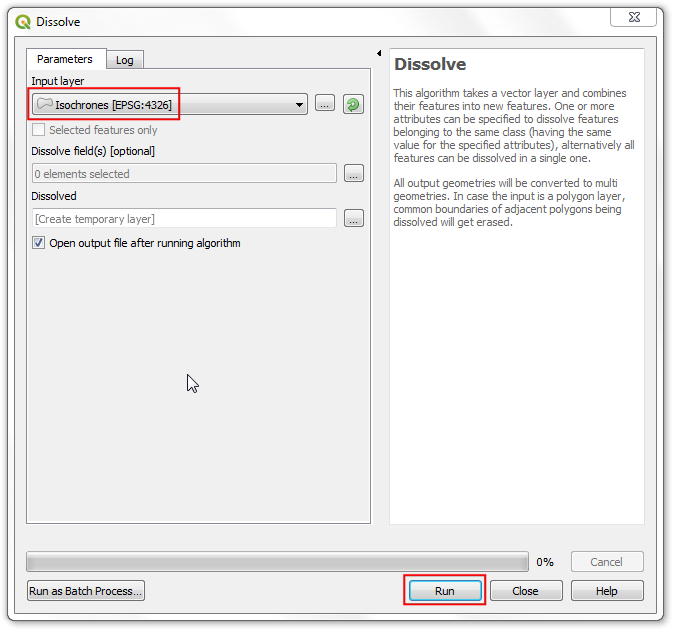
In the Dissolve with Sum, dialog, select
ne_10m_admin_0_countriesas the Input layer,CONTINENTas the Dissolve field andPOP_ESTas the Sum field. Click Run.
Once the processing is finished, click the Close button and switch to the main QGIS window.
You will see the dissolved output layer with one feature for every continent and the total population summed from the individual countries belonging to that continent.
One another advantage of writing processing script is that the methods within the Processing Framework are aware of layer selection and automatically filter your inputs to use only the selected features. This happens because we are defining our input as a
QgsProcessingParameterFeatureSource. A feature source allows use of ANY object which contains vector features, not just a vector layer, so when there are selected features in your layer and ask Processing to use selected features, the input is passed on to your script as aQgsProcessingFeatureSourceobject containing selected features and not the full vector layer. Here’s a quick demonstration of this functionality. Let’s say we want to dissolve only certain continents. Let’s create a selection using Select feature by Expression tool.
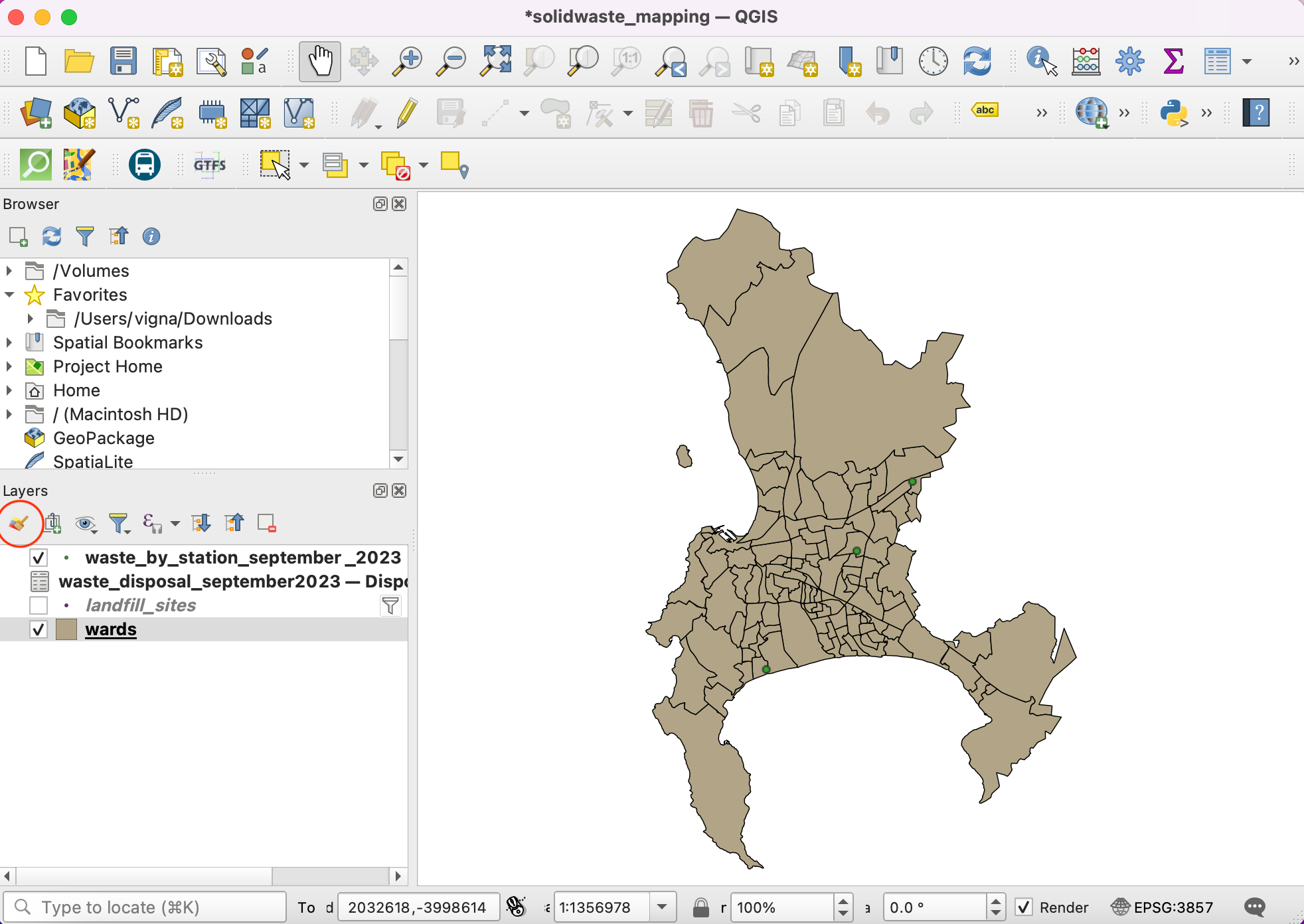
Enter the following expression to select features from North and South America and click Select.
"CONTINENT" = 'North America' OR "CONTINENT" = 'South America'
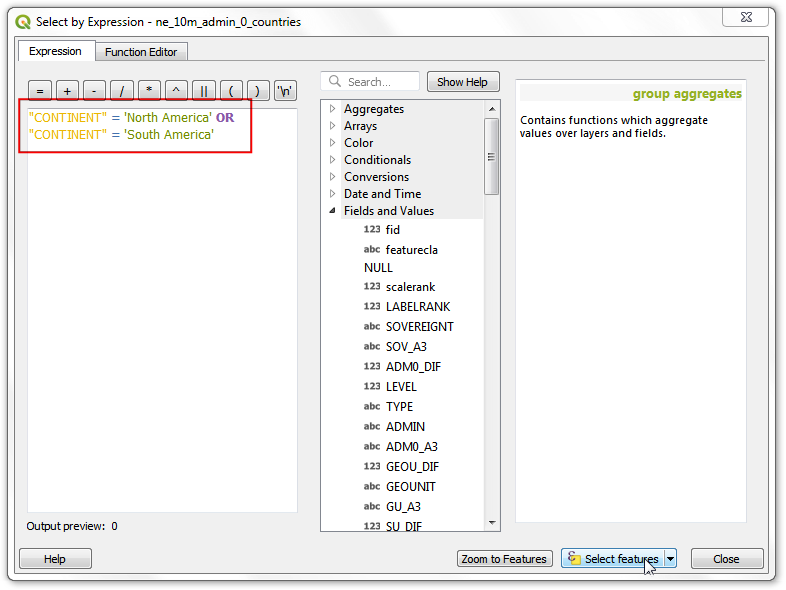
You will see the selected features highlighted in yellow. Locate the
dissolve_with_sumscript and double-click it to run it.
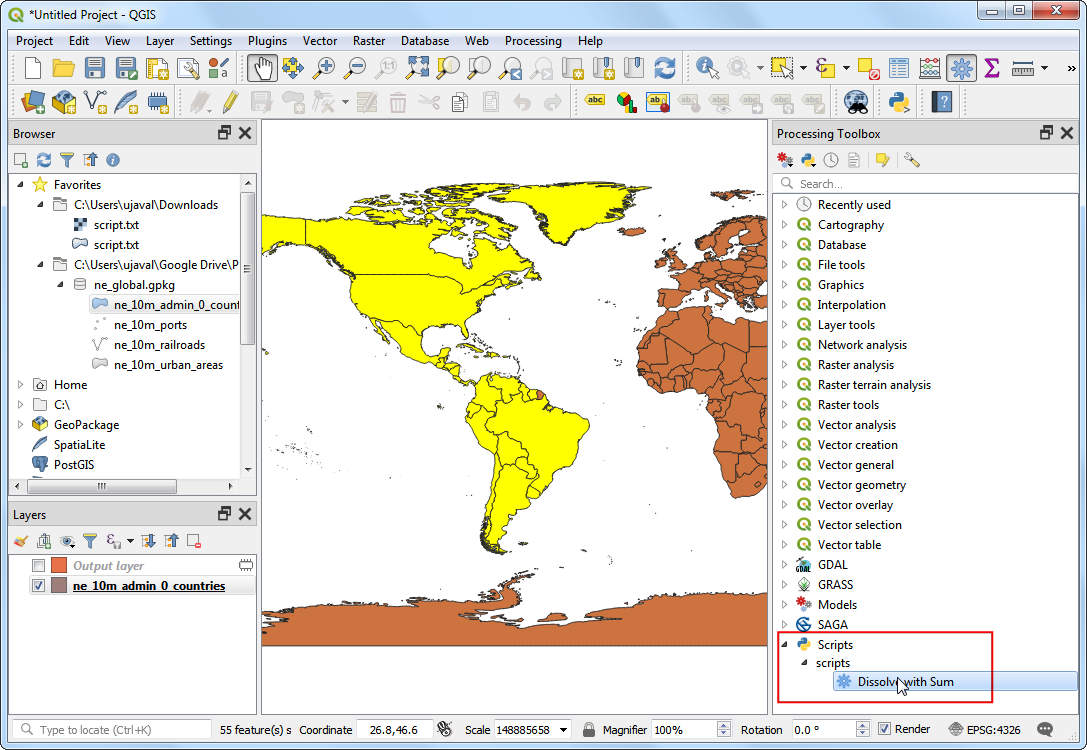
In the Dissolve with Sum dialog, select the
ne_10m_admin_0_countriesas the Input layer. This time, make sure you check the Selected features only box. ChooseSUBREGIONas the Dissolve field andPOP_ESTas the Sum field.
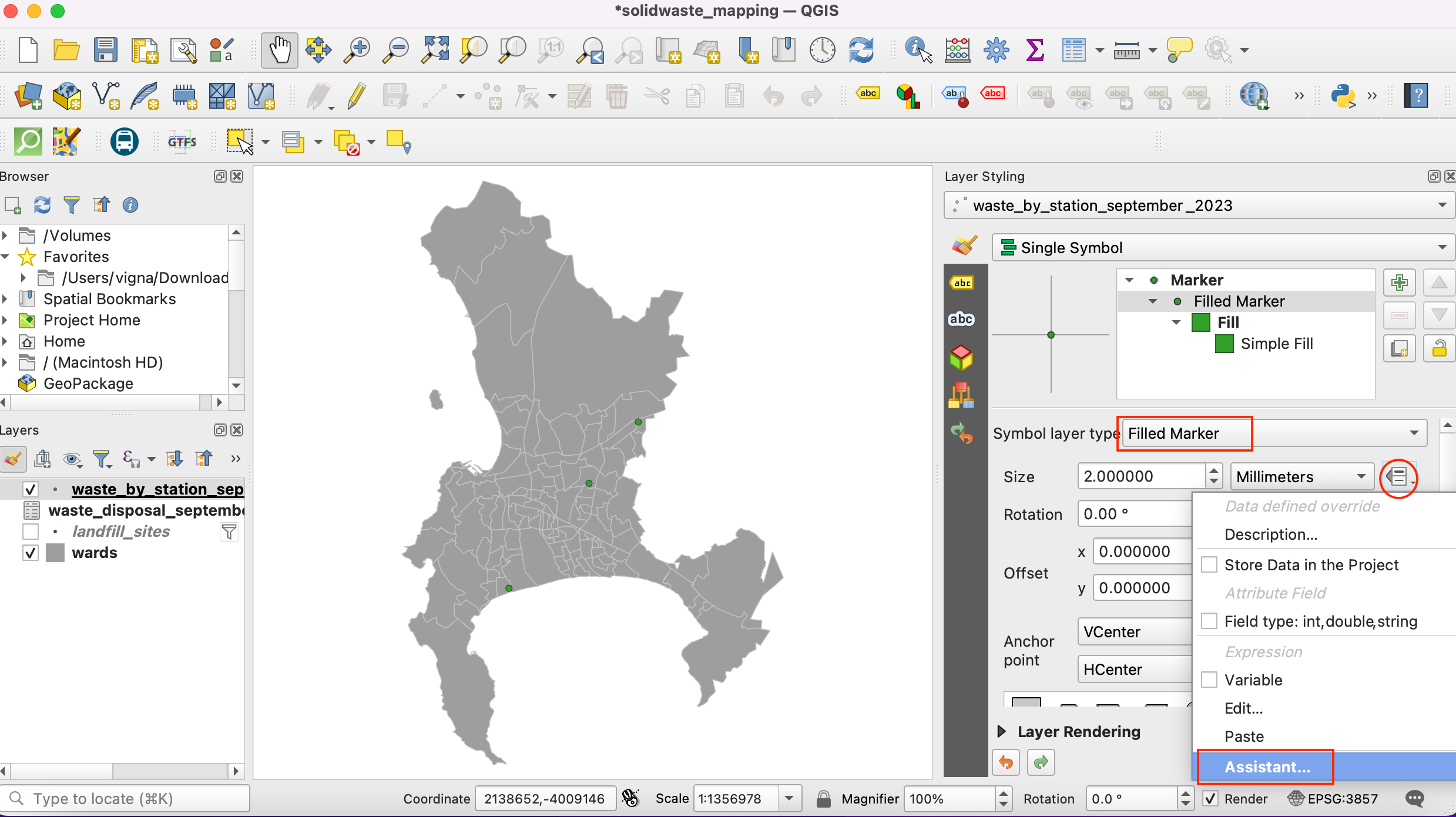
Once the processing finishes, click Close and switch back to the main QGIS window. You will notice a new layer with only the selected features dissolved. Click Identify button and click on a feature to inspect and verify that the script worked correctly.
Below is the complete script for reference. You may modify it to suit your needs.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
***************************************************************************
* *
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify *
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by *
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or *
* (at your option) any later version. *
* *
***************************************************************************
"""
from PyQt5.QtCore import QCoreApplication, QVariant
from qgis.core import (QgsProcessing,
QgsFeatureSink,
QgsFeature,
QgsField,
QgsFields,
QgsProcessingException,
QgsProcessingAlgorithm,
QgsProcessingParameterFeatureSource,
QgsProcessingParameterFeatureSink,
QgsProcessingParameterField,
)
import processing
class DissolveProcessingAlgorithm(QgsProcessingAlgorithm):
"""
Dissolve algorithm that dissolves features based on selected
attribute and summarizes the selected field by cumputing the
sum of dissolved features.
"""
INPUT = 'INPUT'
OUTPUT = 'OUTPUT'
DISSOLVE_FIELD = 'dissolve_field'
SUM_FIELD = 'sum_field'
def tr(self, string):
"""
Returns a translatable string with the self.tr() function.
"""
return QCoreApplication.translate('Processing', string)
def createInstance(self):
return DissolveProcessingAlgorithm()
def name(self):
"""
Returns the algorithm name, used for identifying the algorithm. This
string should be fixed for the algorithm, and must not be localised.
The name should be unique within each provider. Names should contain
lowercase alphanumeric characters only and no spaces or other
formatting characters.
"""
return 'dissolve_with_sum'
def displayName(self):
"""
Returns the translated algorithm name, which should be used for any
user-visible display of the algorithm name.
"""
return self.tr('Dissolve with Sum')
def group(self):
"""
Returns the name of the group this algorithm belongs to. This string
should be localised.
"""
return self.tr('scripts')
def groupId(self):
"""
Returns the unique ID of the group this algorithm belongs to. This
string should be fixed for the algorithm, and must not be localised.
The group id should be unique within each provider. Group id should
contain lowercase alphanumeric characters only and no spaces or other
formatting characters.
"""
return 'scripts'
def shortHelpString(self):
"""
Returns a localised short helper string for the algorithm. This string
should provide a basic description about what the algorithm does and the
parameters and outputs associated with it..
"""
return self.tr("Dissolves selected features and creates and sums values of features that were dissolved")
def initAlgorithm(self, config=None):
"""
Here we define the inputs and output of the algorithm, along
with some other properties.
"""
# We add the input vector features source. It can have any kind of
# geometry.
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterFeatureSource(
self.INPUT,
self.tr('Input layer'),
[QgsProcessing.TypeVectorAnyGeometry]
)
)
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterField(
self.DISSOLVE_FIELD,
'Choose Dissolve Field',
'',
self.INPUT))
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterField(
self.SUM_FIELD,
'Choose Sum Field',
'',
self.INPUT))
# We add a feature sink in which to store our processed features (this
# usually takes the form of a newly created vector layer when the
# algorithm is run in QGIS).
self.addParameter(
QgsProcessingParameterFeatureSink(
self.OUTPUT,
self.tr('Output layer')
)
)
def processAlgorithm(self, parameters, context, feedback):
"""
Here is where the processing itself takes place.
"""
source = self.parameterAsSource(
parameters,
self.INPUT,
context
)
dissolve_field = self.parameterAsString(
parameters,
self.DISSOLVE_FIELD,
context)
sum_field = self.parameterAsString(
parameters,
self.SUM_FIELD,
context)
fields = QgsFields()
fields.append(QgsField(dissolve_field, QVariant.String))
fields.append(QgsField('SUM_' + sum_field, QVariant.Double))
(sink, dest_id) = self.parameterAsSink(
parameters,
self.OUTPUT,
context, fields, source.wkbType(), source.sourceCrs())
# Create a dictionary to hold the unique values from the
# dissolve_field and the sum of the values from the sum_field
feedback.pushInfo('Extracting unique values from dissolve_field and computing sum')
features = source.getFeatures()
unique_values = set(f[dissolve_field] for f in features)
# Get Indices of dissolve field and sum field
dissolveIdx = source.fields().indexFromName(dissolve_field)
sumIdx = source.fields().indexFromName(sum_field)
# Find all unique values for the given dissolve_field and
# sum the corresponding values from the sum_field
sum_unique_values = {}
attrs = [{dissolve_field: f[dissolveIdx], sum_field: f[sumIdx]}
for f in source.getFeatures()]
for unique_value in unique_values:
val_list = [ f_attr[sum_field]
for f_attr in attrs if f_attr[dissolve_field] == unique_value]
sum_unique_values[unique_value] = sum(val_list)
# Running the processing dissolve algorithm
feedback.pushInfo('Dissolving features')
dissolved_layer = processing.run("native:dissolve", {
'INPUT': parameters[self.INPUT],
'FIELD': dissolve_field,
'OUTPUT': 'memory:'
}, context=context, feedback=feedback)['OUTPUT']
# Read the dissolved layer and create output features
for f in dissolved_layer.getFeatures():
new_feature = QgsFeature()
# Set geometry to dissolved geometry
new_feature.setGeometry(f.geometry())
# Set attributes from sum_unique_values dictionary that we had computed
new_feature.setAttributes([f[dissolve_field], sum_unique_values[f[dissolve_field]]])
sink.addFeature(new_feature, QgsFeatureSink.FastInsert)
return {self.OUTPUT: dest_id}
 Ujaval Gandhi
Ujaval Gandhi
If you want to give feedback or share your experience with this tutorial, please comment below. (requires GitHub account)